Introduction.
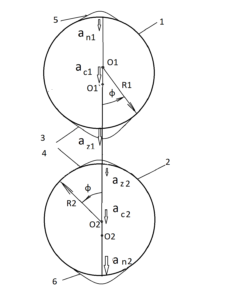
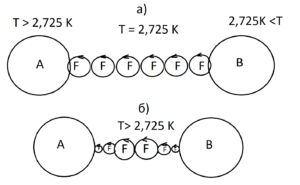
The interaction of the physical vacuum with baryonic matter and radiation is considered on the basis of the proposed law «Interaction of rotating bodies», published in the journal SCI-ARTICLE No. 83 for 2020 [4]. At the same time, additional accelerations (wd1 , wd2) arising near massive bodies, calculated by the formula (4) for simplification are not considered due to their smallness.
The total acceleration of the body (2) in the gravitational field of the central body (1)
a Σ2= a2 + w2 (1)
a2 is the acceleration of the mutual attraction of the second body;
w2 — tidal acceleration;
a Σ 2 =G*M1/R^2 + 2G1*M1* R1*ω1*sin(ω1*t+φ1)/R^3 +2G1*M1*R2*ω2*sin(ω2*t+φ2 )/R^3 (2)
G is the gravitational constant;
G1 is the gravitational constant at the first derivative;
M1, M2 — masses of bodies;
R is the distance between the bodies;
R1 and R2 are the radii of the bodies;
ω1 , ω2 is the angular speed of rotation of bodies;
φ1 , φ2 — initial angles of rotation of bodies;
t — time;
Expression (2) consists of three main terms:
a Σ2 = a 2 + w12 — w22
a 2 =G*M1/R^2-acceleration resulting from the law of universal attraction of I. Newton.
w 12 = 2G1*M1* R1*ω1*sin(ω1*t+ φ1)/R^3 — tidal acceleration of the first body;
— such acceleration is described by the Lenze-Tiering effect, as the entrainment of inertial reference frames by a rotating body.
w 22 = -2G1*M1* R2*ω2*sin(ω2*t+φ2 )/R^3 — tidal acceleration of the second body;
-additional acceleration, assumed by academician A. D. Sakharov, as the effect on the acceleration of the second body only he didn’t realize that the second body was affected by its rotation.
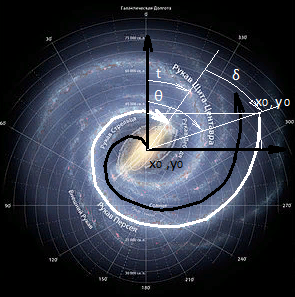
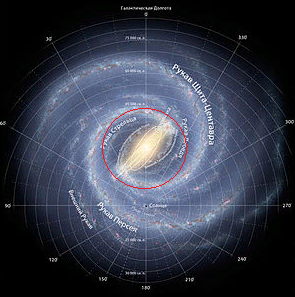
The interaction is considered on the example of the arms of the Centauri Shield and Perseus of the Milky Way galaxy .The physical vacuum is understood as a medium of photons of relic microwave radiation.
Goals and objectives.
The purpose of this paper is to analyze the interaction of baryonic matter with radiation emissions in a physical vacuum environment. The task is to develop a criterion by which it is possible to determine what is currently contained in the concept of «black energy» and «black matter».
Scientific novelty.
According to the author, the linear velocity of a rotating photon determines the speed of light. The structure of the photon, according to the author, is well presented in the article [6] with comments from 28.03.2018.. that is, it is a pair of toroidal vortices united by a strong gravitational interaction. The speed of light is determined by the precessional motion of a pair of toroidal vortices. The proper rotation speed of toroidal vortices is much higher. In the denser environment of the early universe, the speed of light was less important than it is now, which is reflected in the fact that we observe relic light radiation in the microwave range of radio waves. Similarly, it is best to observe the light emission of black holes in the radio range. The speed of light increases over time, and the light emitted in the past, in a denser environment, has a natural redshift, up to the radio range, for relic radiation. The red shift of distant galaxies may indicate not an accelerated expansion of the universe, but an increase in the density of the galaxy’s matter due to its collapse [5].
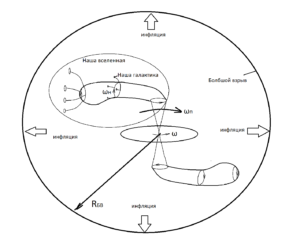
Having a high speed of rotation, the photons of the relic microwave radiation have a high energy. They received their energy in the proto-universe black hole, which is similar to the black hole of a galaxy, but had a much larger size due to the merger of the black holes of galaxies. (Figure 1).

Fig. 1 The formation of Our universe and our galaxy from the proto-universe black hole. Under the influence of precession (wn), the jet of radiation emissions from the event horizon of the future black hole of the proto-universe occupies a significant amount of space — the expansion zone of baryonic matter.
Let us first consider the interaction options for two homogeneous particles:
a Σ2= a2 + w12 — w22= 0-the particles are in orbit around each other, the rotation speeds are very close in magnitude; the forces of attraction and repulsion are equal.
This variant is typical for a physical vacuum, where photons rotate at the speed of light and, despite accelerations close to those of the collision, oscillate near the equilibrium position. Photons rotating at the speed of light are limited in translational and rotational motion by the law of conservation of energy (E = mc ^ 2 where m is the mass of the photon, c is the speed of light), they cannot exceed this energy, and they cannot rotate slower and have less energy than the physical vacuum. It is assumed that the photon becomes visible only when its rotation speed decreases relative to the photons of the surrounding physical vacuum, which is the source of electromagnetic radiation, and the photon has the possibility of translational motion towards neighboring photons. The mass of the photon is converted into the energy of the electromagnetic field and when it is converted back into mass, it has already received a mass displacement, which is equivalent to movement in the gravitational field under the influence of gravitational waves. Gamma radiation is the first to appear, and other types of electromagnetic radiation appear with a further decrease in the speed of rotation. This phenomenon can continue for a very short period of time until the physical vacuum restores the rotation speed of an individual photon, while the speed of neighboring photons decreases, which also become radiation sources, but of a different frequency. The source of the translational motion of the photon, as well as the result of its action on neighboring photons, is the displacement of the center of mass of the photon, which is gravitational in nature and is transmitted from photon to photon in the form of gravitational waves.
a Σ2= a2 + w12 — w22 > 0-the particles attract each other, the difference in the speeds of rotation of the particles is insignificant and the speeds do not exceed the speed of light. The forces of attraction exceed the forces of repulsion. In relative motion, there is a convergence of telephone
This variant is typical for baryonic matter, which collapses matter from the surrounding space.
a Σ2= a2 + w12 — w22 < 0-the particles repel each other, have a significant difference in the speed of rotation, and the speed of rotation exceeds the speed of light. The faster particle (2) is repelled by the lower-speed particle (1), which rushes after the particle (2) and begins to catch up with it when their linear velocities are equalized. In relative motion, in the short term, there is a removal of bodies. In the long run, the bodies will still attract, since the acceleration of universal attraction does not depend on the speed of rotation of the body, and tidal accelerations depend on and decrease with time.
This variant is typical for radiation emissions, the particles of which repel each other and tend to occupy the entire space.
Heterogeneous forms of matter; baryonic and radiative radiation interact through a physical vacuum, but the criterion of interaction remains the same-the linear speed of rotation of the surface of bodies or the outer layer of the vortex of particles on which tidal waves arise under the influence of gravitational waves.
Baryonic matter is based on its origin of hydrogen atoms, which are formed when hadrons of photons of relic microwave radiation, which have oscillations in the form of gravitational waves, are added to the radiation radiation [2].
Radiation hadrons are toroidal vortices [1] that rotate at superluminal speed, so they are repelled by photons, but photons are attracted by hadrons and are joined by them under the influence of gravitational waves. As a result of the addition of photons, a zone of reduced pressure is formed, where the matter that has become baryonic rushes. The photon, which has no freedom of movement in the physical vacuum, has only one way to meet the hadron-to join it. When attached, the direction of rotation of the attached vortex is important; either the direction of its rotation coincides with the direction of the upper layer of the hadron vortex and then there is a weak interaction with the formation of an electron and hydrogen is formed, or the direction of rotation is opposite and then there is a strong interaction and a neutron is formed. The source [2] describes a method for the formation of hydrogen from a neutron and «by a roundabout way.»
A proton and a neutron can combine in a strong interaction and then the proton vortex becomes common to a pair of nucleons and its rotation occurs in the direction of the neutron vortex, so when a pair of nucleons decays, the electron vortex remains behind the neutron, with which it is bound by a strong interaction.
Baryonic matter, which has bound electrons in its composition, can have a linear rotation speed only lower than light, otherwise it will lose electrons. This phenomenon of the decay of matter when exceeding the speed of light is observed on the event horizon of the past of black holes. The decay occurs with the formation of a large number of alpha radiation (α) following the black hole and radiation radiation following the exit from the galaxy in the accelerating gravitational field of the black hole (Fig. 2). More experiments by A. Becquerel showed that as a result of the decay of matter, it is divided into alpha radiation, which is weakly repelled by the Earth’s gravity, gamma radiation (radiation radiation), which is intensively repelled by the Earth’s gravity, and beta radiation, which does not have pronounced gravitational restrictions. The intermediate stages of the decay of matter in the black hole of the proto-universe are: α (alpha particles), t (tritium nuclei) , d (deuterium nuclei), p (protons), n (neutrons) — currently widely represented in the universe. All these decay elements are radiation emissions, behave according to their special properties, and affect the properties of the physical vacuum. It is difficult to predict this behavior, but it can be assumed, for example, that the nuclei of helium atoms absorb photons of the physical vacuum and thereby contract into homogeneous formations of helium, which may represent baryonic matter. This explains the widespread presence of helium in the universe at a size larger than it would be if it were synthesized from hydrogen.
The proton differs from the neutron by the presence of a»shell» in the latter. In the black hole, neutrons fall in the composition of alpha particles together with the» shell», which separates from the neutron and accumulates during the merger of black holes, which serves as the basis for the formation of photons of relic microwave radiation after the Big Bang of the proto-universe black hole.
The source of radiation radiation is also the decay of heavy elements emitted in the form of jets from the event horizon of future black holes. This type of radiation is the product of the expansion of baryonic matter into the surrounding space, like the B. Mandelbrot set. Two jett rays are emitted from one galaxy’s black hole, leading to the formation of at least two new galaxies.
The interaction of the physical vacuum with baryonic matter consists in the reflection (repulsion) of gravitational waves of photons of the relic microwave radiation and in the formation of new gravitational waves around physical bodies. In this case, the baryonic matter is carried away by the physical vacuum in the direction of the propagation of gravitational waves. If there is another physical body in one of the directions of propagation of gravitational waves, photons are displaced from the baseline connecting these bodies, which lowers the pressure and causes the mutual attraction of the bodies.
If one of the directions of propagation of gravitational waves of radiation, the absorption of hadrons of radiation of photons relic of microwave energy on gravitational waves do not pass, but the pressure of the physical vacuum is reduced and baryonic matter is perceived as an attraction to the radiation emissions. It is difficult to judge the strength of this attraction, but given that the rotation speed of hadrons of radiation radiation is much higher than the rotation speed of electrons in baryonic matter, it is possible that the forces of attraction to radiation radiation exceed the forces of mutual attraction to baryonic matter.
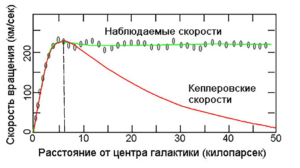
The absorption of photons of relic radiation by radiation radiation is the shielding effect of radiation radiation on gravitational waves. Baryonic matter-of-arms of the galaxy is attracted to the black hole of a galaxy only through matter jumpers and matter sleeves along the chain. Using radiation baryonic matter to be attracted can’t because radiation absorb photons of the CMB, weakening gravitational waves , but the particles of radiation are attracted to each other due to the absorption of photons . This phenomenon is the reason for the constancy of the speed of the stars outside the jumper. Radiation radiation pulls together the arms of galaxies, but can not attract them to the black hole, as they themselves repel it. There is a counter movement of baryonic matter and radiation radiation.

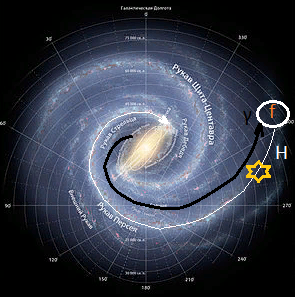
Fig.2 Interaction of baryonic matter and radiation emissions in the Milky Way galaxy. The white color shows the movement of baryonic matter.The black color shows the movement of radiation (γ). The sign (f) shows the addition of a photon by radiation and the formation of hydrogen (H). The asterisk indicates the beginning of star formation.
A significant part of the energy released during nuclear decay at the event horizon of the black hole’s past goes to spin the black hole’s rotor (Fig. 3). The injection of matter for decay is carried out in the regions adjacent to the bridge, the output of the decay products (α-particles) goes in the direction of the black hole rotor, where they are compacted by the tidal forces of the entire accretion disk and in the direction of the exit from the galaxy, where the radiation radiation (γ) is accelerated by the gravitational forces of the black hole. Alpha particles (α) they are the nucleus of helium atoms, where the nucleon pairs are united in the nucleus by a weak interaction, and there is a strong interaction between the neutrons and protons of the nucleon pairs. With increasing pressure and temperature, the nucleon pairs are mutually unwound with decreasing distance and thus store energy that will be released during mutual deceleration with increasing distance. This phenomenon is the main source of the expansion of the universe after the Big Bang. When black holes merge, the masses are combined to the mass of the proto-universe black hole, when it becomes impossible to further increase the mass due to the lack of necessary matter. This is the cause of the Big Bang. In the Big Bang, the entire contents of the proto-universe’s black hole are ejected into space.
In the black hole of the proto-universe, presumably, there were not only alpha particles, but also the products of their decay into smaller homogeneous vortices, from which photons then originated. The same vortices formed toroidal vortices of hadrons, which synthesized the nuclei of superheavy elements, which were radiated from the event horizon of the future black hole of the proto-universe. In the black hole of the proto-universe, hadrons were reformatted to a higher energy level due to an increase in the rotation speed during compression with an increased temperature.
The accretion disk can be considered a stator, and then it, together with the black hole’s rotor, can form an engine, which, according to the type of energy source, can be attributed to photons.

Fig. 3 The photon engine on the example of the Sagittarius-A black hole. The white arrows show the movement of baryonic matter towards the event horizon of the past (indicated by an orange circle). The black arrows show the movement of radiation emissions (γ) to the exit from the galaxy. A red flag with a blue circle in the center indicates the zones of nuclear decay of matter on the event horizon of the past.
The rotation speed (ω) of the galaxy’s black hole can be calculated if we take into account that we know the distance from which the tidal forces begin to prevail (Fig.4). From the tip of the bridge, the nature of the movement of matter changes, the movement takes on an avalanche character. This suggests that a tidal force has been added to the gravitational force, which depends inversely on the cube of the distance.

Fig. 4 Basic dimensions of the Sagittarius-A black hole.
This distance is approximately equal to the radius of the galaxy’s spiral jumper, which is Rр = 10,000 sv. years * 9.46 10 ^ 12 km. = 9.46 10^16 km.
From astronomical observations of scientists, it is known that the radius of the galaxy’s black hole is Rb = 11 10 ^ 6 km.
Let’s take G1= 0.1 G-which corresponds to an ordinary dense cosmic body or a planet like Mercury.
The gravitational accelerations and the tidal acceleration will be equal to:
G * M/R p ^2= 0.1 G* M * R b * ω/R p ^ 3;
where: M is the mass of the black hole.
R p = 0.1 R b * ω ;
ω = Rp / 0.1 Rb = 9,46 10^16 /0,1 * 11 10^6 = 8,6 10^10 volume/ sec. = 86 billion per/ second.
This speed of rotation allows black holes to tear matter into atoms and particles.
According to press reports, modern researchers from Purdue University managed to achieve a rotation speed of a particle of matter in 500 billion revolutions per second.
Conclusions.
As a result of the analysis, it is concluded that the term «dark» can be attributed to particles and matter rotating at light and superluminal speeds, since they cannot be seen with the naked eye. The energy of all transformations in the universe and in the galaxy is due to the energy of the physical vacuum, which can be called «dark energy». «dark matter» can be called radiation radiation, both hadrons from the event horizon of the past of black holes, and heavy element atoms from the event horizon of the future of black holes, which emit hadrons as a result of their decay. «Dark matter» also includes alpha particles and their decay products up to and including hadrons, as well as radiation from the proto-universe black hole at the Big Bang. A strong argument in favor of the fact that it is radiation that is «dark matter» is the experiments of A. Becquerel, who showed that radiation does not react to an electric field.
- Quarks and tidal waves (hypothesis).
- The gravitational nature of electricity and magnetism (hypothesis).
- Reasoning about the structure of a black hole (hypothesis)
- Interaction of the physical vacuum with baryonic matter and radiation emissions (hypothesis)
- Interaction of rotating bodies (hypothesis).
- The effect of a tidal wave on the Earth’s climate (Hypothesis).
Bibliographic list:
1. Atsyukovsky V. A. Popular efirodynamics or how the world in which we live is arranged. Moscow: Publishing House «Scientific World», 2015. Pages 375, Table 2, fig. 120, photos 37, fig. 32.
2. Petrov, The principle of hydrogen formation, [Electronic resource], Access mode URL: petrovvf.livejournal.com/4919 html 2011.11.08;
3. Petrov, Photon. The structure of the photon. The principle of movement. [Electronic resource] Access mode URL: https://petrovvf.livejournal.com/#asset-petrovvf-10505
4. Nechaev A.V. Interaction of rotating bodies, SCI-ARTICLE.RU No. 53 (July) 2020 [Electronic resource ], URL access mode:http://sci-article.ru/stat.php?i=1601963571, (Accessed 27.09.2020);
5. Candidate of Technical Sciences G. S. Lomakin, The nature of redshift. Version 2. [Electronic resource] Access mode: Yandex Zen https://zen.yandex.ru/media/id/5ea6c80450c3275eb74e2f4d/chast-28-priroda-krasnogo-smesceniia-versiia-1-5f7e829e15099c198adc0656 (Accessed 03.12.2020)
6. Kononchenko S. A. Structure of elementary particles (hypothesis), https://sci-article.ru/stat.php?i=1521544132. Article published in No. 56 (April) 2018